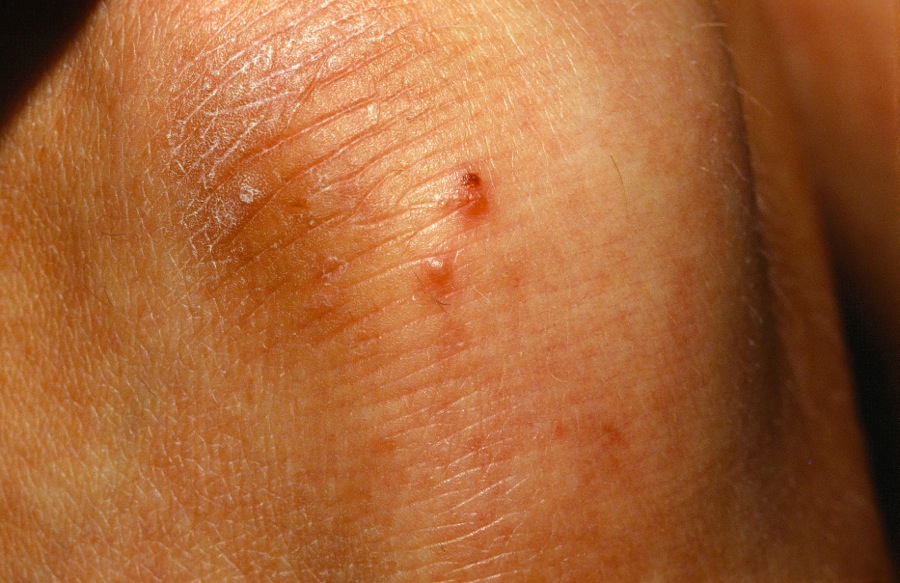
A 35-year-old woman presents with very itchy skin of the knees and forehead. On exam, you see tiny vesicles.

A 35-year-old woman presents with very itchy skin of the knees and forehead. On exam, you see tiny vesicles.
Dermatitis herpetiformis (DH) is an intensely pruritic papulovesicular skin disease caused by gluten sensitivity. Epidermal transglutaminase (eTG) (transglutaminase 3) is the major autoantigen in DH. Tissue transglutaminase (tTG) (transglutaminase 2) is the major autoantigen in celiac disease. IgA antibodies to tissue-transglutaminase (T-TG) form in the gut and cross react with epidermal-TG (e-TG). Deposition of IgA/e-TG complexes in the papillary dermis lead to activation of complement and neutrophils. The average age of onset is between 20 and 40 but children and the elderly may be affected. In Finland, up to 4.4% of DH patients have a first-degree relative with DH and up to 6.1% have relatives with celiac disease (CD). Thus, more than 10% have a relative with DH or CD.
A chronic, intensely pruritic vesicular rash that affects the knees, sacrum, back, posterior axillary folds and the elbows symmetrically is characteristic of DH. Small vesicles or excoriated papules are most common. Mucous membrane involvement is rare. Palmar plantar petechie/purpura can accompany or be the sole manifestation of DH.
Deposition of IgA in a granular pattern at the top of the dermal papilla in both healthy and affected skin is seen. The biopsy of unaffected skin adjacent to an active lesion and sent for DIF is recommended to diagnose DH.
DIF of normal-appearing skin immediately adjacent to a lesion of DH will likely reveal stippling of IgA in the dermal papillae, granular deposition of IgA along the BM, and occasionally granular deposition around blood vessel walls.
Gluten, the causative antigen for the GI disease and the skin, is a protein found in most cereals, e.g. wheat, barley, oats, malt and rye--and not rice and corn. Interestingly, patch testing with a potassium iodine mixture may produce bulla.
Homepage | Who is Dr. White? | Privacy Policy | FAQs | Use of Images | Contact Dr. White