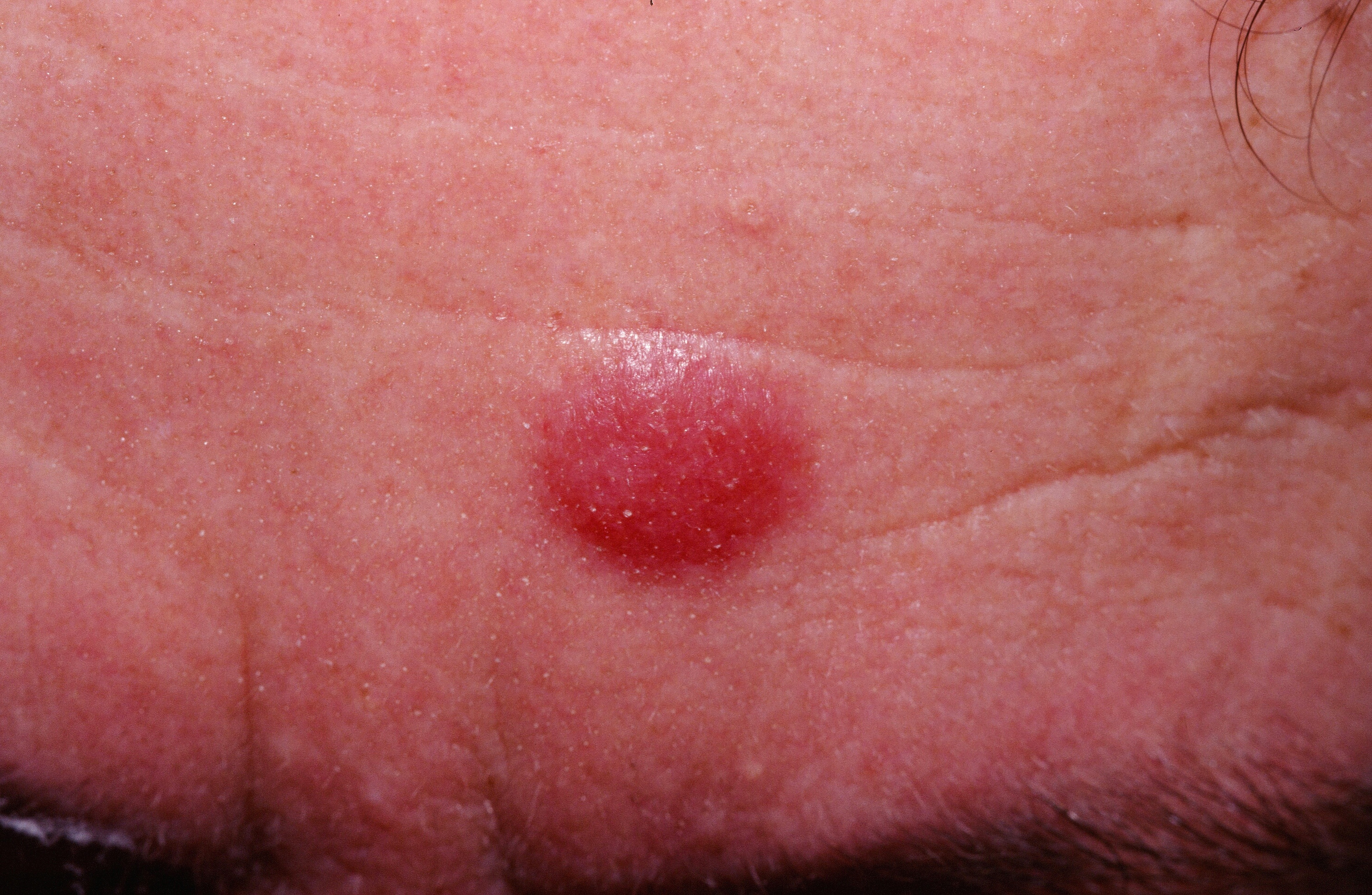
Lymphocytoma cutis (aka pseudolymphoma) is a dermal collection of lymphocytes and other inflammatory cells. The key initial intervention is to exclude malignancy, e.g. leukemia or lymphoma cutis. There are reports of lymphocytoma cutis eventuating into a B-cell lymphoma. In some cases, particularly in Europe, Borrelia has been associated. Various drugs have been reported to stimulate lesions that mimic lymphoma, so called drug-induced pseudolymphoma.
A 0.5 -2 cm, asymptomatic, erythematous to plum-colored papule or nodule is characteristic. They may occur virtually anywhere with a special predilection for the ear lobes. A miliarial type occurs.
B cell: reactive to bites, piercings tattoo dyes, drugs, borrelia
T cell: The erythrodermic pseudolymphoma (T-cell pattern) typifies drug-induced pseudolymphoma, which is most often secondary to anticonvulsant therapy.
4 mm punch biopsy with immunohistologic staining. Clonal gene rearrangement analysis can also be done. Rule out Borrelia.
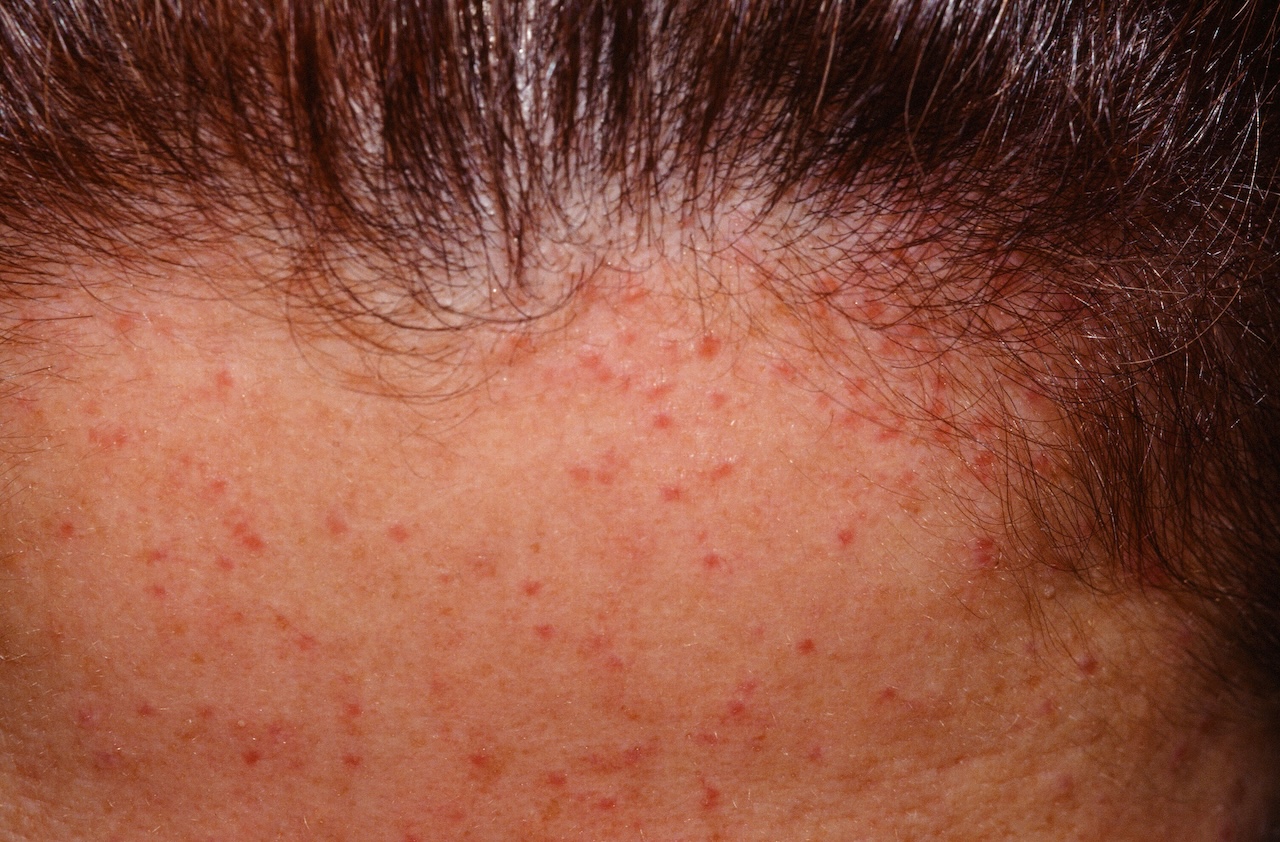
Pseudolymphoma, the miliarial type.
Homepage | Who is Dr. White? | Privacy Policy | FAQs | Use of Images | Contact Dr. White